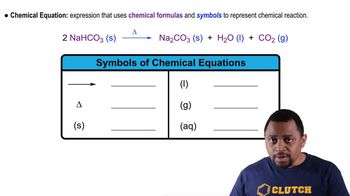
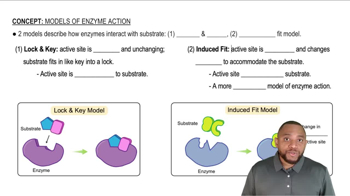
Which of these terms, (i) mixture, (ii) solid, (iii) liquid, (iv) gas, (v) chemical element, (vi) chemical compound, applies to the following substances at room temperature?
a. Gasoline
b. Iodine
c. Water
d. Air
e. Blood
f. Sodium bicarbonate
g. Gaseous ammonia
h. Silicon