
Glucose, also known as "blood sugar" when measured in blood, has the formula C6H12O6.
a. Write the equation for the combustion of glucose with O2 to give CO2 and H2O.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Combustion Reaction
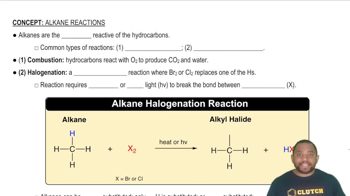
Chemical Equation

Stoichiometry

Acetylene (H–C≡C–H) is the fuel used in welding torches.
b. Estimate ∆H for this reaction (in kJ/mol) using the bond energies listed in Table 7.1.
Nitrogen in air reacts at high temperatures to form NO2 according to the following reaction: N2 + 2 O2 → 2 NO2
b. Estimate ∆H for this reaction (in kcal and kJ) using the bond energies from Table 7.1.
Glucose, also known as "blood sugar" when measured in blood, has the formula C6H12O6.
c. What is the minimum amount of energy (in kJ) a plant must absorb to produce 15.0 g of glucose?
Which of the following processes results in an increase in entropy of the system?
a. A drop of ink spreading out when it is placed in water
b. Steam condensing into drops on windows
c. Constructing a building from loose bricks
For each of the following processes, specify whether entropy increases or decreases. Explain each of your answers.
a. Assembling a jigsaw puzzle
