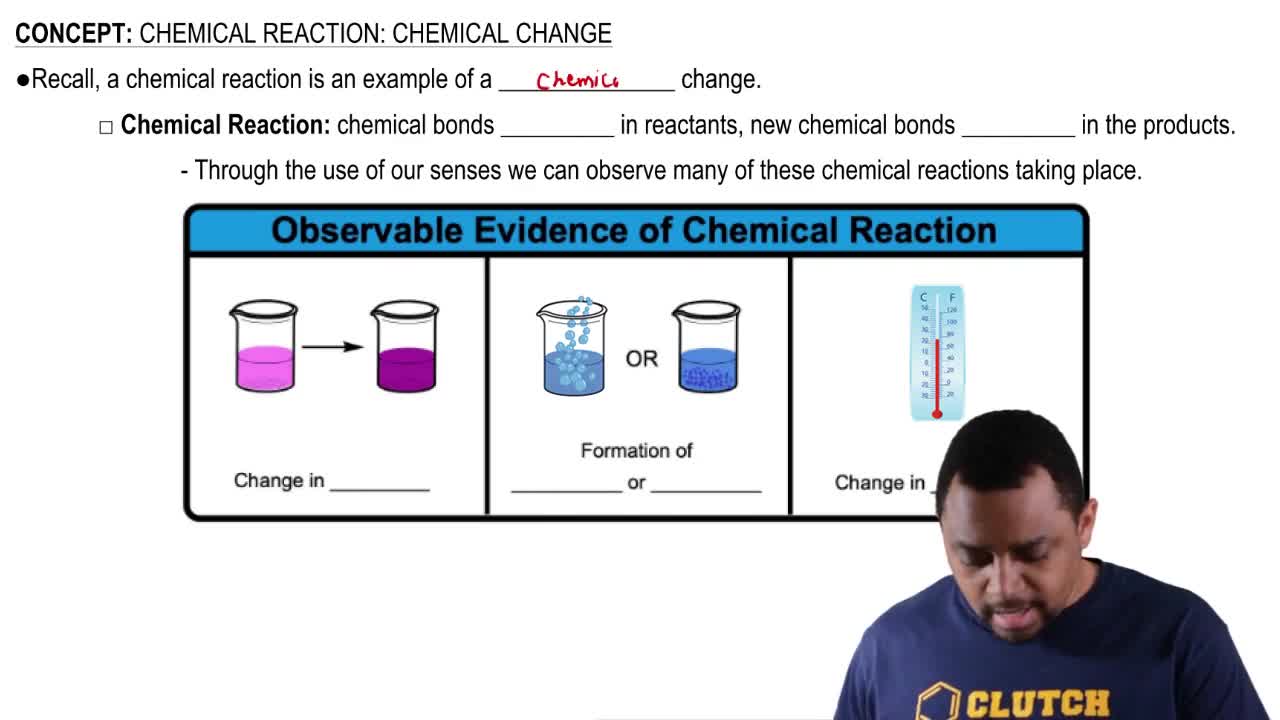
The following diagram portrays a reaction of the type A(s) → B(g) + C(g), where the different-colored spheres represent different molecular structures. Assume that the reaction has ∆H = +9.1 kcal/mol (+38.1 kJ/mol).
a. What is the sign of ∆S for the reaction?