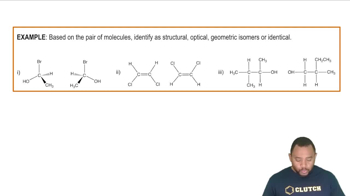
Textbook Question
Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a. 3-Methyl-1-heptene
b. 4,4-Dimethyl-2-pentyne
c. 2-Methyl-3-hexene
d. 1,3,3-Trimethylcyclohexene
945
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a. 3-Methyl-1-heptene
b. 4,4-Dimethyl-2-pentyne
c. 2-Methyl-3-hexene
d. 1,3,3-Trimethylcyclohexene
Classify the following reactions as an addition, elimination, or substitution:
a. CH3Br + NaOH → CH3OH + NaBr
b. H2C═CH2 + HCl → CH3CH2Cl
c. CH3CH2Br → H2C═CH2 + HBr
Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
a. Fumaric acid to malic acid
Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
b. 2-Phosphoglyceric acid to phosphoenolpyruvic acid