Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a. 3-Methyl-1-heptene
b. 4,4-Dimethyl-2-pentyne
c. 2-Methyl-3-hexene
d. 1,3,3-Trimethylcyclohexene

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a. 3-Methyl-1-heptene
b. 4,4-Dimethyl-2-pentyne
c. 2-Methyl-3-hexene
d. 1,3,3-Trimethylcyclohexene
Which of the following substances exist as can cis–trans isomers? Draw both isomers for those that do.
a. 2,3-Dimethyl-2-pentene (condensed structures only)
b. 2-Methyl-2-hexene (both condensed and line structures)
c. 2-Hexene (line structures only)
Classify the following reactions as an addition, elimination, or substitution:
a. CH3Br + NaOH → CH3OH + NaBr
b. H2C═CH2 + HCl → CH3CH2Cl
c. CH3CH2Br → H2C═CH2 + HBr
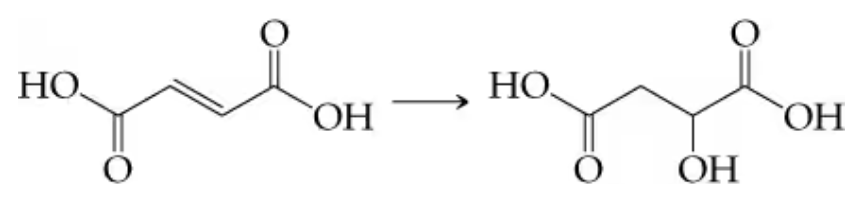
Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
b. 2-Phosphoglyceric acid to phosphoenolpyruvic acid
Draw all possible products formed when 2-methyl-2-butene undergoes addition with HCl. Label them as being either the major or the minor product.
In the following addition reactions, are the given alkyl halides obtained as the major products? Give a reason for your answer.
a. 3-Chloro-3-ethylpentane from addition of HCl to 3-ethyl-2-pentene