Textbook Question
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
a. Octanal
b. Methyl phenyl ketone
c. 4-Methylhexanal
d. Methyl tert-butyl ketone
1105
views

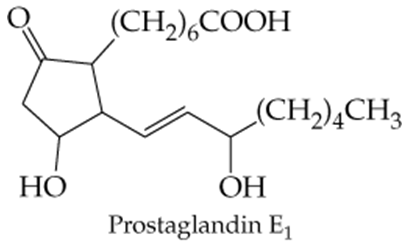
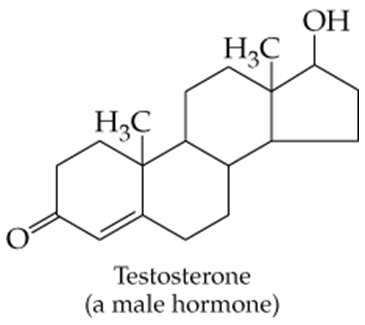
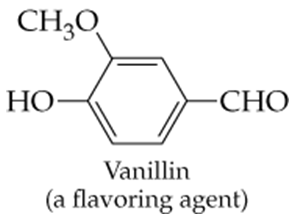
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
a. Octanal
b. Methyl phenyl ketone
c. 4-Methylhexanal
d. Methyl tert-butyl ketone
Give systematic, IUPAC names for the following compounds. Redraw each in line structure format.
a.
b.
c.
d. Dipropyl ketone
For each compound shown next (a–d), indicate whether the compound is polar or nonpolar, and whether it is soluble or insoluble in water.
a.
b.
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
d.