Explain what bonds must be made or broken and where the electrons go when the hydrogen-bonded water between the two amines shown on page 507 reacts to form an amine, ammonium ion, and OH⁻.
Ch.16 Amines

Chapter 16, Problem 32b
Name the following amines, and identify them as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
b. 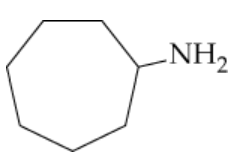
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the structure of the amine provided in the image. Identify the nitrogen atom and count the number of carbon-containing groups (alkyl or aryl groups) directly attached to it. This will help determine if the amine is primary, secondary, or tertiary.
Recall the definitions: A primary amine has one alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen, a secondary amine has two, and a tertiary amine has three. Use this information to classify the amine.
Identify the longest carbon chain attached to the nitrogen atom. This chain will serve as the parent chain for naming the amine.
Number the parent chain starting from the carbon closest to the nitrogen atom. Assign the position of the nitrogen atom and any substituents on the chain.
Combine the name of the parent chain with the suffix '-amine' and include the positions of substituents, if any. If the amine is secondary or tertiary, list the additional alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen in alphabetical order as prefixes.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified based on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen atom: primary amines have one carbon group, secondary amines have two, and tertiary amines have three. Understanding the structure of amines is crucial for naming them and identifying their classification.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amine Classification Example 1
Nomenclature of Amines
The nomenclature of amines follows specific rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). The naming typically involves identifying the longest carbon chain attached to the nitrogen and using suffixes or prefixes to denote the presence of the amine group. For example, a primary amine with a two-carbon chain is named ethylamine, while a tertiary amine with three carbon groups is called triethylamine.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amine Classification Example 1
Classification of Amines
Amines are classified into three categories based on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Primary amines have one carbon group, secondary amines have two, and tertiary amines have three. This classification affects their chemical properties and reactivity, making it essential to identify the type of amine when analyzing their behavior in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
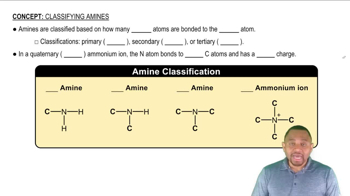
Amine Classification Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1613
views
Textbook Question
Complete the following equations:
b.
1359
views
Textbook Question
Draw the structures corresponding to the following names:
a. N-Methylpentylamine
134
views
Textbook Question
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a.
608
views
Textbook Question
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a.
661
views
Textbook Question
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
c. N-Butyl-N-isopropylhexylammonium chloride
577
views
