For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
b. Ionized zinc is attached to this protein so the protein can function.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

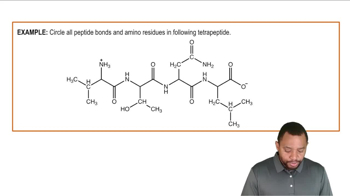

For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
b. Ionized zinc is attached to this protein so the protein can function.
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
c. Phosphate groups are attached to this protein.
Both α-keratin and tropocollagen have helical secondary structure. How do these molecules differ in (a) amino acid composition and (b) three-dimensional structure?
If the same peptide found in Problem 18.32 is subjected to acid hydrolysis, how many fragments will result? Why?
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
a. Val
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
d. Glu-Asp