Why is ∆G a useful quantity for predicting the favorability of biochemical reactions?

What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Catabolism
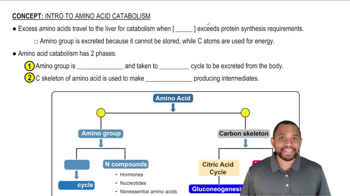
Anabolism

Metabolism

The following reactions occur during the catabolism of acetyl-CoA. Which are exergonic? Which is endergonic? Which reaction produces a phosphate that later yields energy by giving up a phosphate group?
c. L-Malate + NAD+ → Oxaloacetate + NADH + H+
∆G = +17 kcal/mol (+129.3 kJ/mol)
The following reactions occur during the catabolism of glucose. Which are exergonic? Which is endergonic? Which proceeds farthest toward products at equilibrium?
b. Phosphoenol pyruvate + H2O → Pyruvate + Phosphate(Pi)
∆G = –14.8 kcal/mol (–61.9 kJ/mol)
What is the difference between digestion and metabolism?
Arrange the following events in the order in which they occur in a catabolic process: electron transport, digestion, oxidative phosphorylation, citric acid cycle.
What key metabolic intermediate is formed from the catabolism of all three major classes of foods: carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins?
