Textbook Question
What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
1699
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

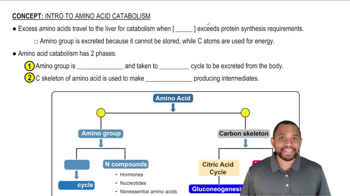

What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
What is the difference between digestion and metabolism?
Arrange the following events in the order in which they occur in a catabolic process: electron transport, digestion, oxidative phosphorylation, citric acid cycle.
Why is ATP sometimes called a high-energy molecule?
What general kind of chemical reaction does ATP participate in?
What does it mean when we say that two reactions are coupled?