Textbook Question
What tetrapeptide is synthesized from the informational DNA sequence G-T-C-A-G-T-A-C-G-T-T-A?
679
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


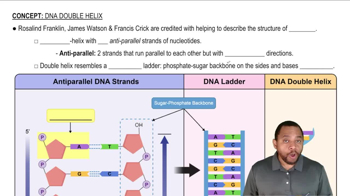
What tetrapeptide is synthesized from the informational DNA sequence G-T-C-A-G-T-A-C-G-T-T-A?
What is the general shape and structure of a tRNA molecule?
There are different tRNAs for each amino acid. What is one major way to differentiate among the tRNAs for each amino acid?
Suppose that 22% of the nucleotides of a DNA molecule are deoxyadenosine and during replication the relative amounts of available deoxynucleoside triphosphates are 22% dATP, 22% dCTP, 28% dGTP, and 28% dTTP. What deoxynucleoside triphosphate is limiting to the replication? Explain.