Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

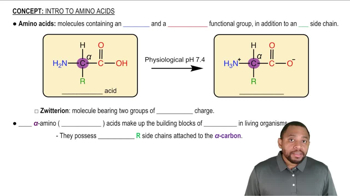

Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val
If the sequence T-A-C-C-C-T appears on the informational strand of DNA, what sequence appears opposite it on the template strand? Label your answer with 3′ and 5′ ends.
What tetrapeptide is synthesized from the informational DNA sequence G-T-C-A-G-T-A-C-G-T-T-A?
There are different tRNAs for each amino acid. What is one major way to differentiate among the tRNAs for each amino acid?
Insulin is synthesized as preproinsulin, which has 81 amino acids. How many heterocyclic bases must be present in the informational DNA strand to code for preproinsulin (assuming no introns are present)?
Suppose that 22% of the nucleotides of a DNA molecule are deoxyadenosine and during replication the relative amounts of available deoxynucleoside triphosphates are 22% dATP, 22% dCTP, 28% dGTP, and 28% dTTP. What deoxynucleoside triphosphate is limiting to the replication? Explain.