Textbook Question
Write the full name of:
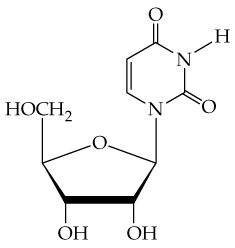
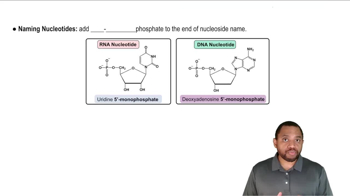
a. dUMP
1213
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write the full name of:
a. dUMP
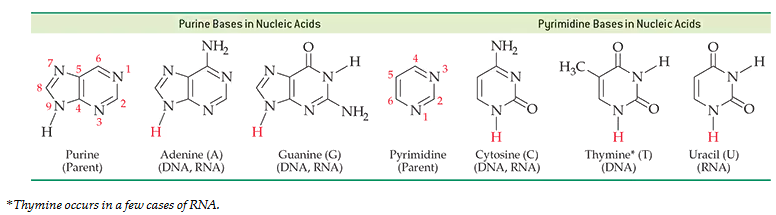
Name the bases in the pentanucleotide with the sequence G-A-U-C-A. Does this come from RNA or DNA? Explain.
Write the complementary sequence of bases for each DNA strand shown next.
a. 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′