Textbook Question
Name the nucleoside shown here. Copy the structure, and number the C and N atoms (refer to Table 26.1).
525
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
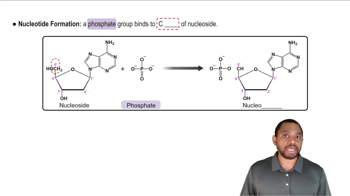


Name the nucleoside shown here. Copy the structure, and number the C and N atoms (refer to Table 26.1).
Write the full name of:
a. dUMP
Write the complementary sequence of bases for each DNA strand shown next.
a. 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′
Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.