Back
BackProblem 1
Compare pathogenicity with virulence.
Problem 2
How are capsules and cell wall components related to pathogenicity? Give specific examples.
Problem 3
Describe how hemolysins, leukocidins, coagulase, kinases, hyaluronidase, siderophores, and IgA proteases might contribute to pathogenicity.
Problem 4
Explain how drugs that bind each of the following would affect pathogenicity:
a. Iron in the host's blood
b. N. gonorrhoeae fimbriae
c. S. pyogenes M protein
Problem 5
Compare and contrast the following aspects of endotoxins and exotoxins: bacterial source, chemistry, toxigenicity, and pharmacology. Give an example of each toxin.
Problem 6
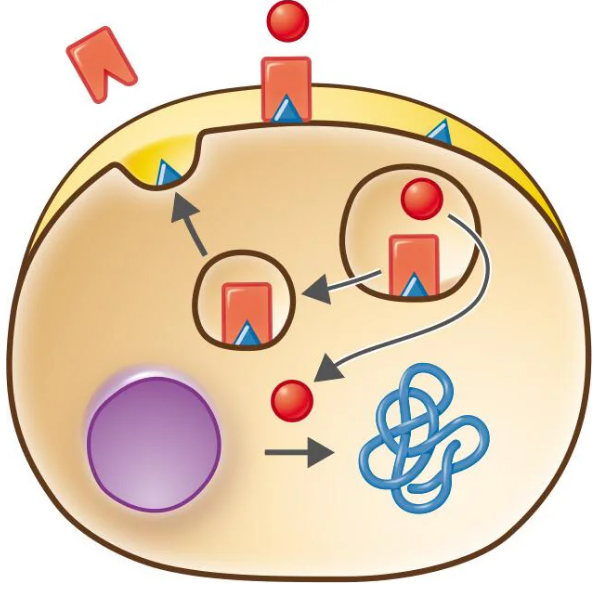
Label this diagram to show how the Shiga toxin enters and inhibits protein synthesis in a human cell.
Problem 7
Describe the factors contributing to the pathogenicity of fungi, protozoa, and helminths.
Problem 8
Which of the following genera is the most infectious?
Problem 9
How can viruses and protozoa avoid being killed by the host’s immune response?
Problem 10
The Opa gene is used to identify this endotoxin-producing bacterium that grows well in the high- CO₂ conditions inside phagocytes.
Problem 1
The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms?
a. C. tetani
b. E. coli
c. S. enterica
d. S. mutans
e. C. botulinum
Problem 2
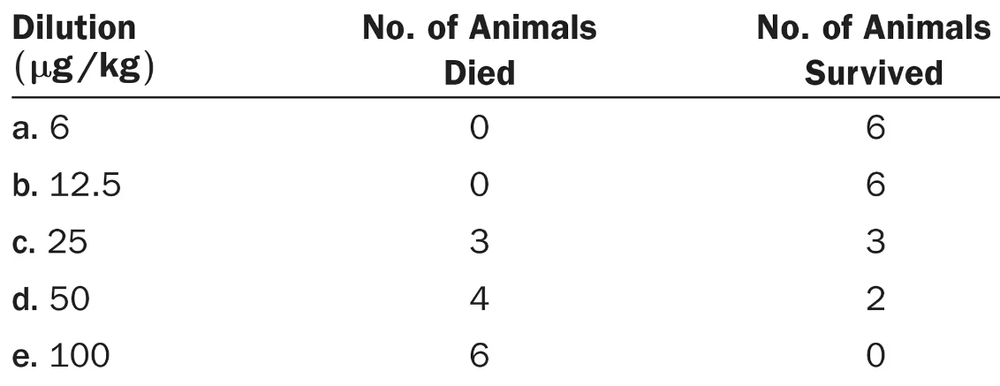
What is the LD₅₀ for the bacterial toxin tested in the following example?
Problem 3
Which of the following is not a portal of entry for pathogens?
a. Mucous membranes of the respiratory tract
b. Mucous membranes of the digestive canal
c. Skin
d. Blood
e. Parenteral route
Problem 4
All of the following are related to bacterial infection. Which would prevent all of the others?
a. Vaccination against fimbriae
b. Phagocytosis
c. Inhibition of phagocytic digestion
d. Destruction of adhesins
e. Alteration of cytoskeleton
Problem 5
The ID₅₀ for Campylobacter sp. is 500 cells; the ID₅₀ for Cryptosporidium sp. is 100 cells. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Both microbes are pathogens.
b. Both microbes produce infections in 50% of the inoculated hosts.
c. Campylobacter is more virulent than Cryptosporidium.
d. Campylobacter and Cryptosporidium are equally virulent; they cause infections in the same number of test animals.
e. Cryptosporidium infections are acquired more easily than Campylobacter infections.
Problem 7
A drug that binds to mannose on human cells would prevent
a. the entrance of Vibrio enterotoxin.
b. the attachment of pathogenic E. coli.
c. the action of botulinum toxin.
d. streptococcal pneumonia.
e. the action of diphtheria toxin.
Problem 8
The earliest smallpox vaccines were infected tissue rubbed into the skin of a healthy
person. The recipient of such a vaccine usually developed a mild case of smallpox, recovered, and was immune thereafter. What is the most likely reason this vaccine did not kill more people?
a. Skin is the wrong portal of entry for smallpox.
b. The vaccine consisted of a mild form of the virus.
c. Smallpox is normally transmitted by skin-to-skin contact.
d. Smallpox is a virus.
e. The virus mutated.
Problem 9
Which of the following does not represent the same mechanism for avoiding host defenses as the others?
a. Rabies virus attaches to the receptor for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
b. Salmonella attaches to the receptor for epidermal growth factor.
c. Lymphocryptovirus (mononucleosis) virus binds to the host receptor for complement protein.
d. Surface protein genes in N. gonorrhoeae mutate frequently.
e. none of the above
Problem 10
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The primary goal of a pathogen is to kill its host.
b. Evolution selects for the most virulent pathogens.
c. A successful pathogen doesn't kill its host before it is transmitted.
d. A successful pathogen never kills its host.