Back
BackProblem 1
What is industrial microbiology? Why is it important?
Problem 2
How does commercial sterilization differ from sterilization procedures used in a hospital or laboratory?
Problem 3
Why is a can of blackberries preserved by commercial sterilization typically heated to 100°C instead of at least 116°C?
Problem 4
Outline the steps in the production of cheese, and compare the production of hard and soft cheeses.
Problem 5
Beer is made with water, malt, and yeast; hops are added for flavor. What is the purpose of the water, malt, and yeast? What is malt?
Problem 6
Why is a bioreactor better than a large flask for industrial production of an antibiotic?
Problem 7
The manufacture of paper includes the use of bleach and formaldehyde-based glue. The microbial enzyme xylanase whitens paper by digesting dark lignins. Oxidase causes the fibers to stick together, and cellulase will remove ink. List three advantages of using these microbial enzymes over traditional chemical methods for making paper.
Problem 8
Describe an example of bioconversion. What metabolic processes can result in fuels?
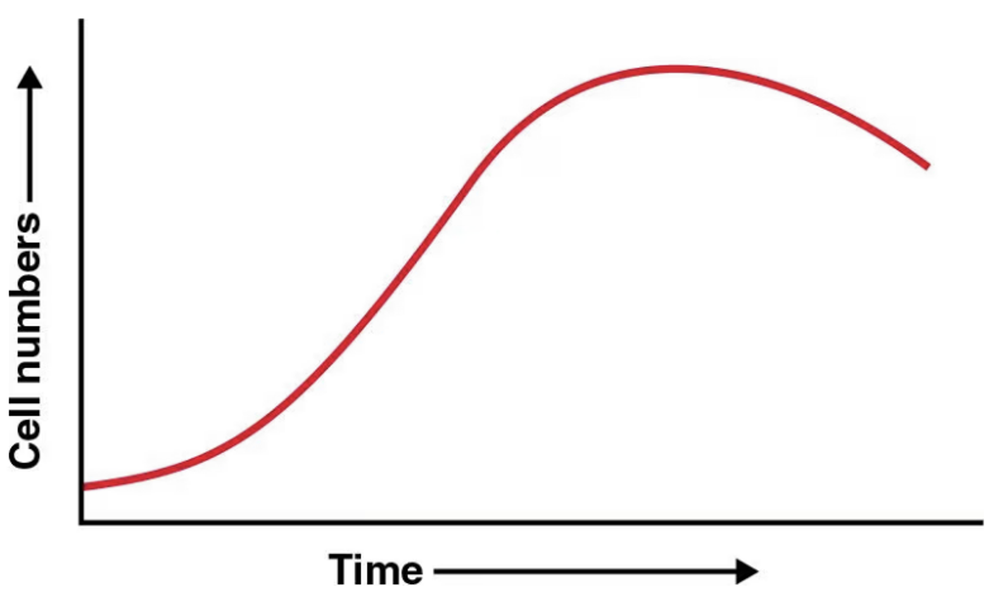
Problem 9
Label the trophophase and idiophase in this graph. Indicate when primary and secondary metabolites are formed.
Problem 10
Van Leeuwenhoek was the first to see this budding microbe with a nucleus and cell wall; although humans have used it since before the beginning of recorded history, Louis Pasteur was the first to figure out what it does.
Problem 1
Foods packed in plastic for microwaving are
a. Dehydrated.
b. Freeze-dried.
c. Packaged aseptically.
d. Commercially sterilized.
e. Autoclaved.
Problem 2
Acetobacter is necessary for only one of the steps of vitamin C manufacture. The easiest way to accomplish this step would be to
a. Add substrate and Acetobacter to a test tube
b. Affix Acetobacter to a surface and run substrate over it
c. Add substrate and Acetobacter to a bioreactor
d. Find an alternative to this step
e. None of the above
Problem 3
Use the following choices to answer the following question:
a. Bacillus coagulans
b. Byssochlamys
c. Flat sour spoilage
d. Lactobacillus
e. Thermophilic anaerobic spoilage
The spoilage of canned foods due to inadequate processing, accompanied by gas production.
Problem 4
Use the following choices to answer the following question:
a. Bacillus coagulans
b. Byssochlamys
c. Flat sour spoilage
d. Lactobacillus
e. Thermophilic anaerobic spoilage
The spoilage of canned foods caused by G. stearothermophilus.
Problem 6
The term 12D treatment refers to
a. Heat treatment sufficient to kill 12 bacteria.
b. The use of 12 different treatments to preserve food.
c. A 1012 reduction in C. botulinum endospores.
d. Any process that destroys thermophilic bacteria.
Problem 7
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms?
a. Algal oil
b. Ethanol
c. Hydrogen
d. Methane
e. Uranium
Problem 8
Which type of radiation is used to preserve foods?
a. Ionizing
b. Nonionizing
c. Radiowaves
d. Microwaves
e. All of the above
Problem 9
Which of the following reactions is undesirable in winemaking?
a. Sucrose → ethanol
b. Ethanol → acetic acid
c. Malic acid → lactic acid
d. Glucose → pyruvic acid
Problem 10
Which of the following reactions is an oxidation carried out by A. ferrooxidans?
a. Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺
b. Fe³⁺ → Fe²⁺
c. CuS→ CuSO₄
d. Fe⁰ → Cu⁰
e. None of the above