Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence.
The graph of y = sin (x + π/4) is obtained by shifting the graph of y = sin x ______ unit(s) to the ________ (right/left).

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
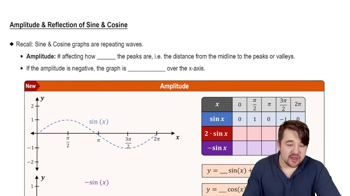

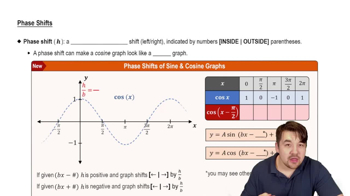
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence.
The graph of y = sin (x + π/4) is obtained by shifting the graph of y = sin x ______ unit(s) to the ________ (right/left).
An object in simple harmonic motion has position function s(t), in inches, from an equilibrium point, as follows, where t is time in seconds.
𝒮(t) = 5 cos 2t
What is the amplitude of this motion?
Graph each function over a one-period interval.
y = 3 sec [(1/4)x]
Match each function with its graph in choices A–I. (One choice will not be used.)
y = cos (x - π/4)
A. <IMAGE> B. <IMAGE> C. <IMAGE>
D. <IMAGE> E. <IMAGE> F. <IMAGE>
G. <IMAGE> H. <IMAGE> I. <IMAGE>
For each function, give the amplitude, period, vertical translation, and phase shift, as applicable.
y = 3 cos (x + π/2)