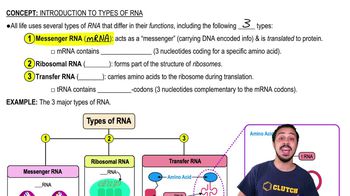
During the process of transcription, ________.
a. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of more DNA.
b. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA.
c. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.
d. RNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.