Which of these is not a property of all living organisms?
a. Capable of reproduction
b. Uses energy
c. Composed of multiple cells
d. Responds to the environment

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 1 Biology: The Study of Scientific Life
Ch. 1 Biology: The Study of Scientific Life Problem 6
Problem 6 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
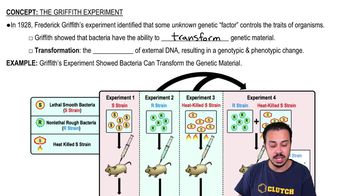

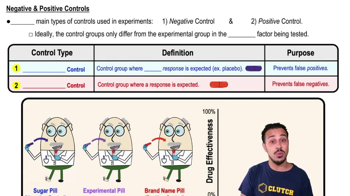
Which of these is not a property of all living organisms?
a. Capable of reproduction
b. Uses energy
c. Composed of multiple cells
d. Responds to the environment
Which of the following statements best distinguishes hypotheses from theories in science?
a. Theories are hypotheses that have been proven.
b. Hypotheses usually are narrow in scope; theories have broad explanatory power.
c. Hypotheses are tentative guesses; theories are correct answers to questions about nature.
d. Hypotheses and theories are different terms for essentially the same thing in science.
Which of the following best demonstrates the unity among all living organisms?
a. Structure correlated with function
b. DNA and a common genetic code
c. Emergent properties
d. Natural selection
Which of the following is a true statement of observational data?
a. It is always qualitative, not quantitative.
b. It is used to form hypotheses, but not to test them.
c. It can include comparisons of fossils as well as DNA sequences.
d. It is the type of data used for the independent variable in a controlled experiment.
A biologist studying interactions among the bacteria in an ecosystem could not be working at which level in life's hierarchy? (Choose carefully and explain your answer.)
a. The population level
b. The molecular level
c. The organism level
d. The organ level
Which of the following best describes the logic of scientific inquiry?
a. If I generate a testable hypothesis, my experiments will support it.
b. If my prediction is correct, it will lead to a testable hypothesis.
c. If my observations are accurate, they will support my hypothesis.
d. If my hypothesis is correct, I can expect certain test results.