Fill in the following concept map to review the processes by which molecules move across membranes.
<IMAGE?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

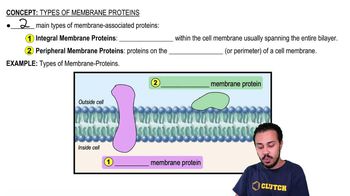
Fill in the following concept map to review the processes by which molecules move across membranes.
<IMAGE?
Label the parts of the following diagram illustrating the catalytic cycle of an enzyme.
A plant cell placed in distilled water will ______________; an animal cell placed in distilled water will ______________.
a. Burst … burst
b. Become flaccid … shrivel
c. Become turgid … be normal in shape
d. Become turgid … burst
The sodium concentration in a cell is 10 times less than the concentration in the surrounding fluid. How can the cell move sodium out of the cell? (Explain your answer.)
a. Passive transport
b. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
c. Active transport
d. Facilitated diffusion
The synthesis of ATP from ADP and
a. Stores energy in a form that can drive cellular work
b. Involves the hydrolysis of a phosphate bond
c. Transfers a phosphate, priming a protein to do work
d. Is an exergonic process