Back
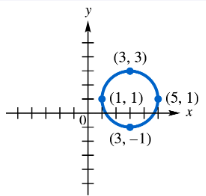
BackProblem 23
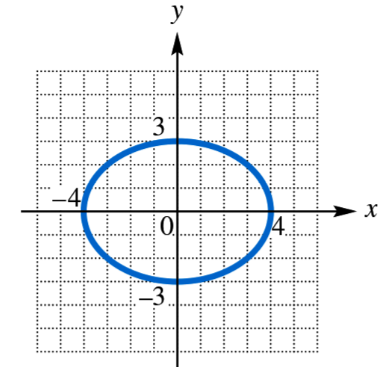
Use each graph to determine an equation of the circle in (a) center-radius form and (b) general form.
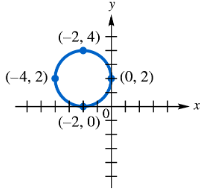
Problem 25
Use each graph to determine an equation of the circle in (a) center-radius form and (b) general form.
Problem 27
Give the center and radius of the circle represented by each equation. x2+y2+6x+8y+9=0
Problem 29
Give the center and radius of the circle represented by each equation. x2+y2-4x+12y=-4
Problem 35
Describe the graph of each equation as a circle, a point, or nonexistent. If it is a circle, give the center and radius. If it is a point, give the coordinates. x2+y2+2x-6y+14=0
Problem 36
Describe the graph of each equation as a circle, a point, or nonexistent. If it is a circle, give the center and radius. If it is a point, give the coordinates. x2+y2+4x-8y+32=0
Problem 38
Describe the graph of each equation as a circle, a point, or nonexistent. If it is a circle, give the center and radius. If it is a point, give the coordinates. x2+y2+4x+4y+8=0
Problem 39
Describe the graph of each equation as a circle, a point, or nonexistent. If it is a circle, give the center and radius. If it is a point, give the coordinates. x2+y2-2x+12y-12=0
Problem 41
Describe the graph of each equation as a circle, a point, or nonexistent. If it is a circle, give the center and radius. If it is a point, give the coordinates. x2+y2+4x+14y=-54
Problem 48
Work each of the following. Find the equation of a circle with center at (-4, 3), passing through the point (5, 8).Write it in center-radius form.
Problem 1
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. The domain of the relation { (3,5), (4, 9), (10, 13) } is _____.
Problem 3
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. The equation y = 4x - 6 defines a function with independent variable______ and dependent variable ________ .
Problem 5
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. For the function ƒ(x) = -4x + 2, ƒ(-2)= ______.
Problem 11
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(5,1),(3,2),(4,9),(7,8)}
Problem 12
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(8,0),(5,7),(9,3),(3,8)}
Problem 13
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(2,4),(0,2),(2,6)}
Problem 14
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(9,-2),(-3,5),(9,1)}
Problem 15
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(-3,1),(4,1),(-2,7)}
Problem 16
Determine whether each relation defines a function. {(-12,5),(-10,3),(8,3)}
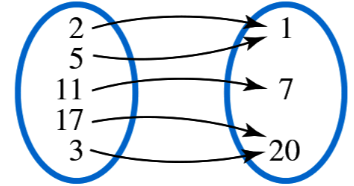
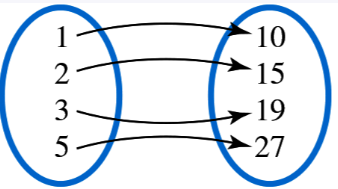
Problem 17
Determine whether each relation defines a function.
Problem 18
Determine whether each relation defines a function.
Problem 19
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range. {(1,1),(1,-1),(0,0),(2,4),(2,-4)}
Problem 20
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range. {(2,5),(3,7),(3,9),(5,11)}
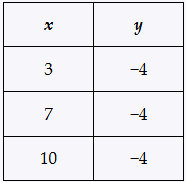
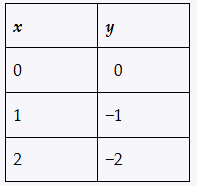
Problem 21
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
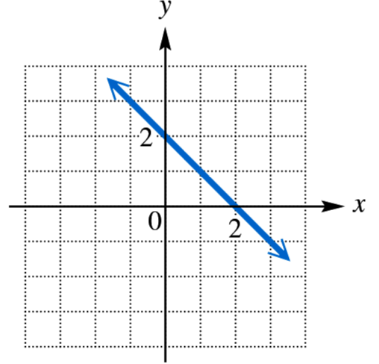
Problem 22
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
Problem 23
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
Problem 24
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
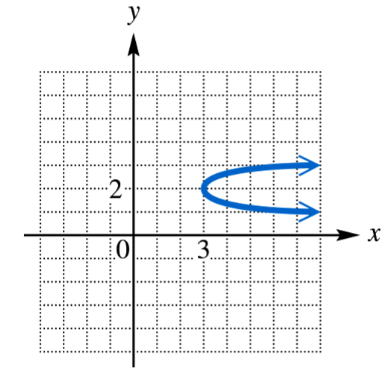
Problem 27
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
Problem 29
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.
Problem 30
Determine whether each relation defines a function, and give the domain and range.