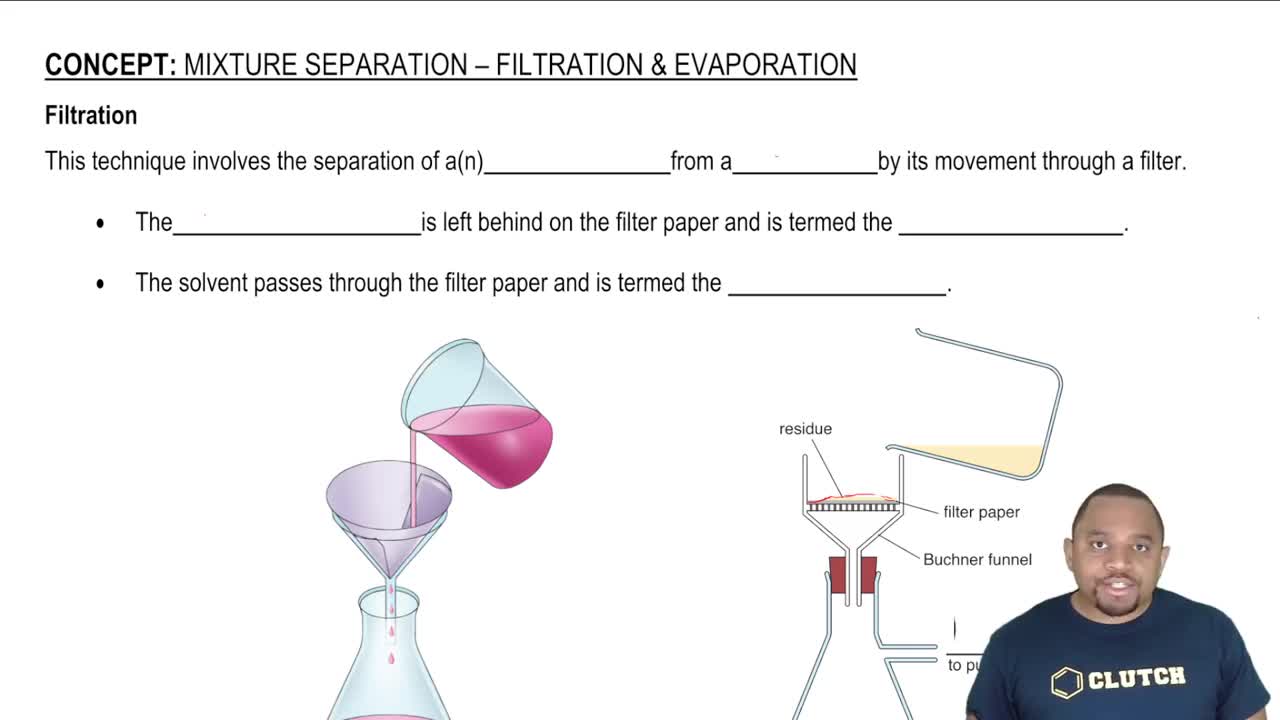
Evaporation Rate
The evaporation rate is the speed at which molecules transition from the liquid phase to the vapor phase. Factors influencing evaporation include temperature, surface area, and intermolecular forces. In this scenario, acetone, with its lower boiling point and weaker intermolecular forces, will evaporate more quickly than water, despite the volume differences.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance