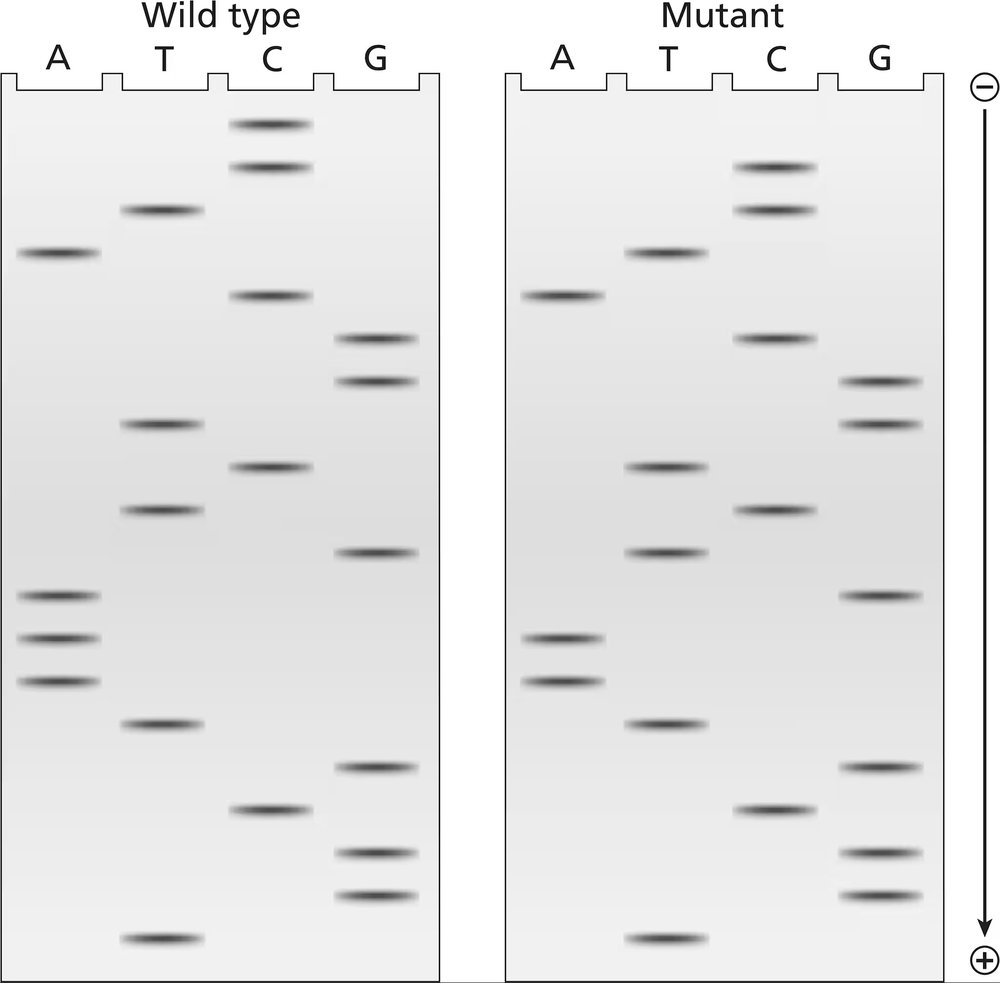
Common baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is normally grown at 37°C, but it will grow actively at temperatures down to approximately 25°C. A haploid culture of wild-type yeast is mutagenized with EMS. Cells from the mutagenized culture are spread on a complete-medium plate and grown at 25°C. Six colonies (1 to 6) are selected from the original complete-medium plate and transferred to two fresh complete-medium plates. The new complete plates (shown) are grown at 25°C and 37°C. Four replica plates are made onto minimal medium or minimal plus adenine from the 25°C complete-medium plate. The new plates are grown at either 25°C or 37°C and the growth results are shown.
What can you say about colony 4?