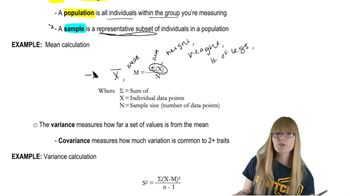
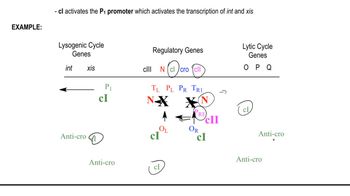
In pea plants, the appearance of flowers along the main stem is a dominant phenotype called 'axial' and is controlled by an allele T. The recessive phenotype, produced by an allele t, has flowers only at the end of the stem and is called 'terminal.' Pod form displays a dominant phenotype, 'inflated,' controlled by an allele C, and a recessive 'constricted' form, produced by the c allele. A cross is made between a pure-breeding axial, constricted plant and a plant that is pure-breeding terminal, inflated.
Suppose that all of the F₂ progeny with terminal flowers, i.e., plants with terminal flowers and inflated pods and plants with terminal flowers and constricted pods, are saved and allowed to self-fertilize to produce a partial F₃ generation. What is the expected phenotypic distribution among these F₃ plants?