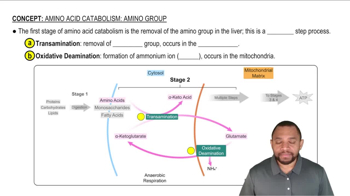
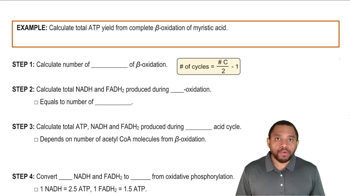
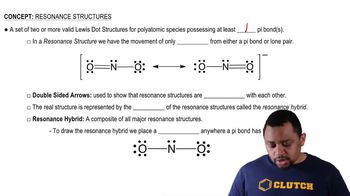
Textbook Question
The pancreatic proteases are synthesized and stored as zymogens. They are activated after the pancreatic juices enter the small intestine. Why is it essential that these enzymes be synthesized and stored in their inactive forms?
520
views