Which of the following contains a coordinate covalent bond? (Hint: How many covalent bonds would you expect the central atom (underlined/bold) to form?)
a. PbCl2
b. Cu(NH3)42+
c. NH4+

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
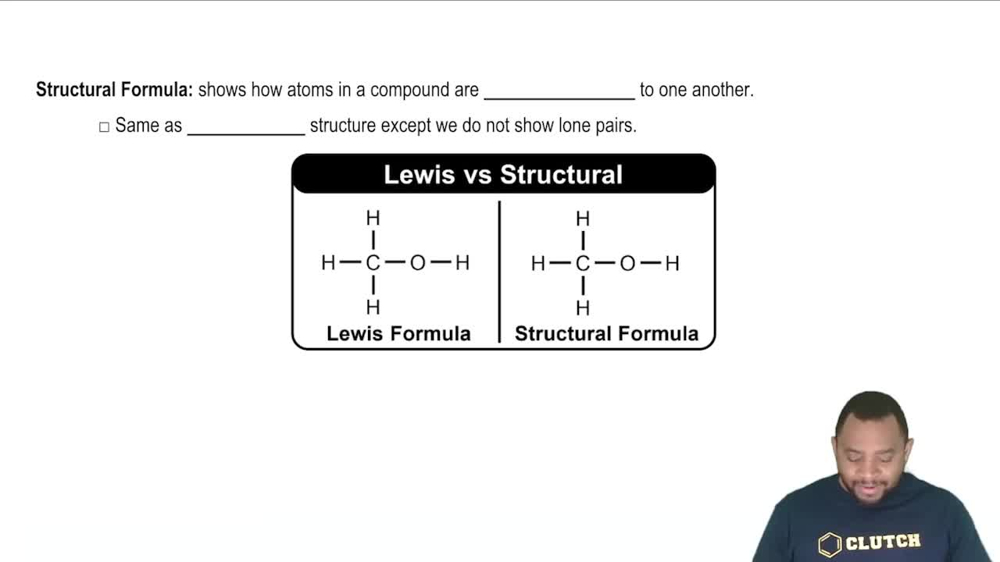

Which of the following contains a coordinate covalent bond? (Hint: How many covalent bonds would you expect the central atom (underlined/bold) to form?)
a. PbCl2
b. Cu(NH3)42+
c. NH4+
Write electron-dot symbols to show the number of covalent bonds and the lone pairs of electrons in the molecules that are formed by reactions between the atoms in Problem 4.34.
a. Aluminum and bromine
b. Carbon and fluorine
c. Cesium and iodine
d. Zinc and fluorine
e. Lithium and chlorine
A compound of gallium with chlorine has a melting point of 77°C and a boiling point of 201°C. Is the compound ionic or covalent? What is a likely formula?
Distinguish between the following:
c. A lone pair and a shared pair of electrons
Consider the following possible structural formulas for C3H6O2. If a structure is not reasonable, explain what changes could be made to convert it to a reasonable structure.
a.
Expand the following condensed structures into the correct structural formulas.
c. CH3CH2OCH2Cl