Textbook Question
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
a. Ala—Asn—Thr
b. DS
971
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

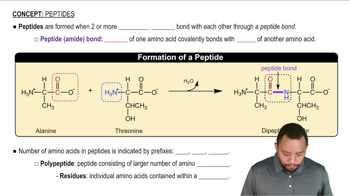
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
a. Ala—Asn—Thr
b. DS
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
c. Val—Arg
Identify the N-terminus and the C-terminus for each of the peptides in Problem 10.18.
d. IYP
Name the stabilizing attractive force found in secondary structures of proteins.
When a protein folds into its tertiary structure, does the primary structure change? Explain.
Describe the differences in the shape of an α helix and a β-pleated sheet.