Textbook Question
CRISPR was first discovered as a defense mechanism in what organism?
1415
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


CRISPR was first discovered as a defense mechanism in what organism?
Name the gene that tags other genes through fluorescent coloring.
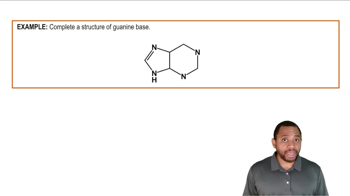
Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
b. adenine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
c. dGMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
a. dTMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
d. GMP