Textbook Question
Name the gene that tags other genes through fluorescent coloring.
856
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
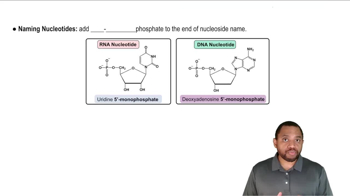
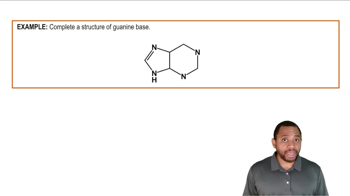
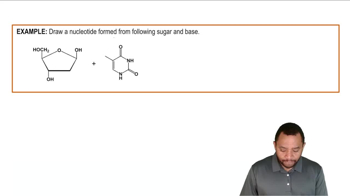
Name the gene that tags other genes through fluorescent coloring.
Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
b. adenine
Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
e. guanine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
a. dTMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
d. GMP
How do the bases thymine and uracil differ?