Textbook Question
Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
e. guanine
659
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
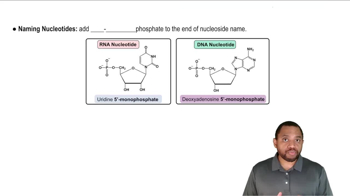
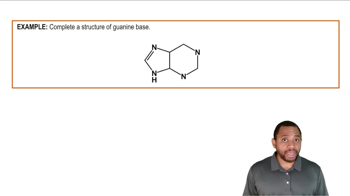

Identify each of the following bases as a pyrimidine or a purine:
e. guanine
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
c. dGMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
a. dTMP
How do the bases thymine and uracil differ?
Fill in the following table comparing structural similarities between proteins and nucleic acids:
Write the complementary base sequence for each of the following DNA segments. Indicate the 5' and the 3' ends.
b. 5'ATAGCCCTTACTGG3'