Textbook Question
Indicate whether the following processes represent anabolism or catabolism.
b. synthesis of fats
575
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Indicate whether the following processes represent anabolism or catabolism.
b. synthesis of fats
Indicate whether the following processes represent anabolism or catabolism.
b. generation of ATP from breakdown of fructose
Name the types of chemical reactions that tend to be found in anabolic pathways.
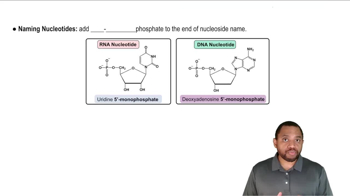
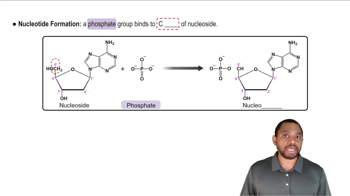
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. contains a form of the vitamin niacin
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. exchanges energy when a phosphate bond is hydrolyzed
Using abbreviations (not structures), write the reaction of flavin adenine dinucleotide that gives off energy (–∆G) .