Textbook Question
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(d)
624
views

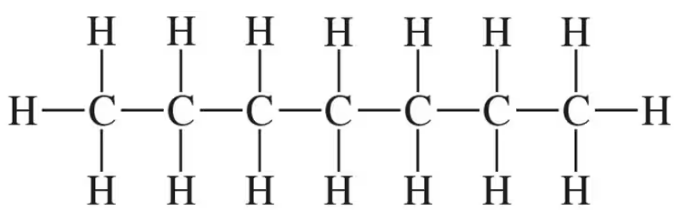
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(d)
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(b)
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(d)
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(a)
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(c)
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH