Textbook Question
Give the skeletal structure and name of the straight-chain alkanes whose molecular formula is shown.
(b) C10H22
1391
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
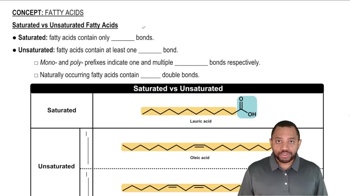

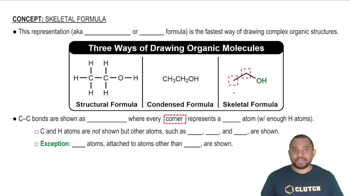
Give the skeletal structure and name of the straight-chain alkanes whose molecular formula is shown.
(b) C10H22
Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C6H12 and contains a five-membered ring
Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C7H14 and contains a six-membered ring
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(a)
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(b)
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(b)