Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(b)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
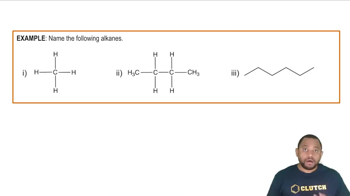

Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(b)
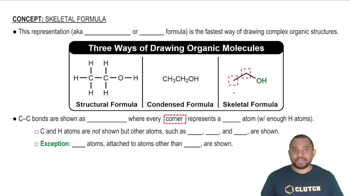
Lewis structures, condensed structural formulas, and skeletal structures are used to represent the structure of an organic compound. Each of the following compounds is shown in one of these representations. Convert each compound into the other two structural representations not shown.
(c)
Alkanes are also referred to as saturated hydrocarbons. Explain the meaning of the term hydrocarbon. Why are alkanes called saturated hydrocarbons?
Give the skeletal structure and name of the straight-chain alkanes whose molecular formula is shown.
(b) C10H22
Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C6H12 and contains a five-membered ring
Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C7H14 and contains a six-membered ring