Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b)

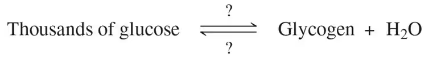
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b)
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(a)
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b)
How do low-carb diets work? We store glucose molecules in our muscles and liver as glycogen, which consists of thousands of glucose molecules linked together. During periods of fasting, we can activate glycogen to provide glucose.
(b) Individuals who do not eat carbohydrates do not store the same levels of glycogen as people who do. Explain the weight loss associated with storing less glycogen.
The reverse reaction of hydration is dehydration. The dehydration of an alcohol involves removing an OH from one carbon and an H from the carbon next to it to form an alkene. In glycolysis, the enzyme enolase catalyzes the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), which contains a carbon–carbon double bond. Complete the reaction below by drawing the structure of PEP.