Textbook Question
Draw a possible hydrogen bond between a molecule of cholesterol and a molecule of water.
815
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
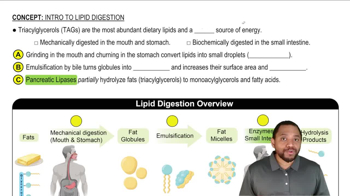

Draw a possible hydrogen bond between a molecule of cholesterol and a molecule of water.
Compare the structure of a soap molecule to a phospholipid and explain why a soap’s polar head is smaller than that of a phospholipid.
Describe other components present in a cell membrane and their relative location.
Fats and oils are both triglycerides. Consider the shortening Crisco®. Would scientists consider this a fat or an oil? What about margarine?