Magnetite, an iron ore with formula Fe3O4, can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen to yield iron metal and water vapor.
d. This reaction has K = 2.3 × 10-18. Are the reactants or the products favored?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
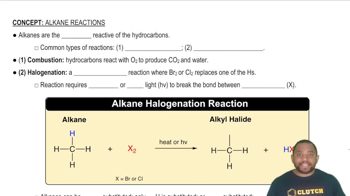


Magnetite, an iron ore with formula Fe3O4, can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen to yield iron metal and water vapor.
d. This reaction has K = 2.3 × 10-18. Are the reactants or the products favored?
For the evaporation of water, H2O(l) → H2O(g), at 100°C, ∆H = +9.72 kcal/mol (+40.7 kJ/mol).
b. How many kilojoules are released when 10.0 g of H2O(g) is condensed?
Ammonia reacts slowly in air to produce nitrogen monoxide and water vapor:
NH3(g) + O2(g) ⇌ NO(g) + H2O(g) + Heat
b. Write the equilibrium equation.
Sketch an energy diagram for a system in which the forward reaction has Eact = +25 kcal/mol (+105 kJ/mol) and the reverse reaction has Eact = +35 kcal/mol (+146 kJ/mol).
a. Is the forward process endergonic or exergonic?
Obtain a package of your favorite snack food and examine the nutritional information on the label. Confirm the caloric value listed by using the conversions listed in the table in the Chemistry in Action feature 'Energy from Food' (p. 191). Alternatively, you can use the estimates for caloric value for a given food as provided in the table.
b. How long would you have to engage in each of the physical activities to burn the calories contained in your snack?