How is volume/volume percent concentration defined and for what types of solutions is it typically used?

How many moles of each substance are needed to prepare the following solutions?
a. 50.0 mL of 8.0% (m/v) KCl (MW = 74.55 g/mol)
b. 200.0 mL of 7.5% (m/v) acetic acid (MW = 60.05 g/mol)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Molarity and Moles
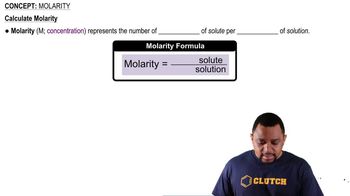
Percent by Mass/Volume (m/v)

Dilution and Solution Preparation
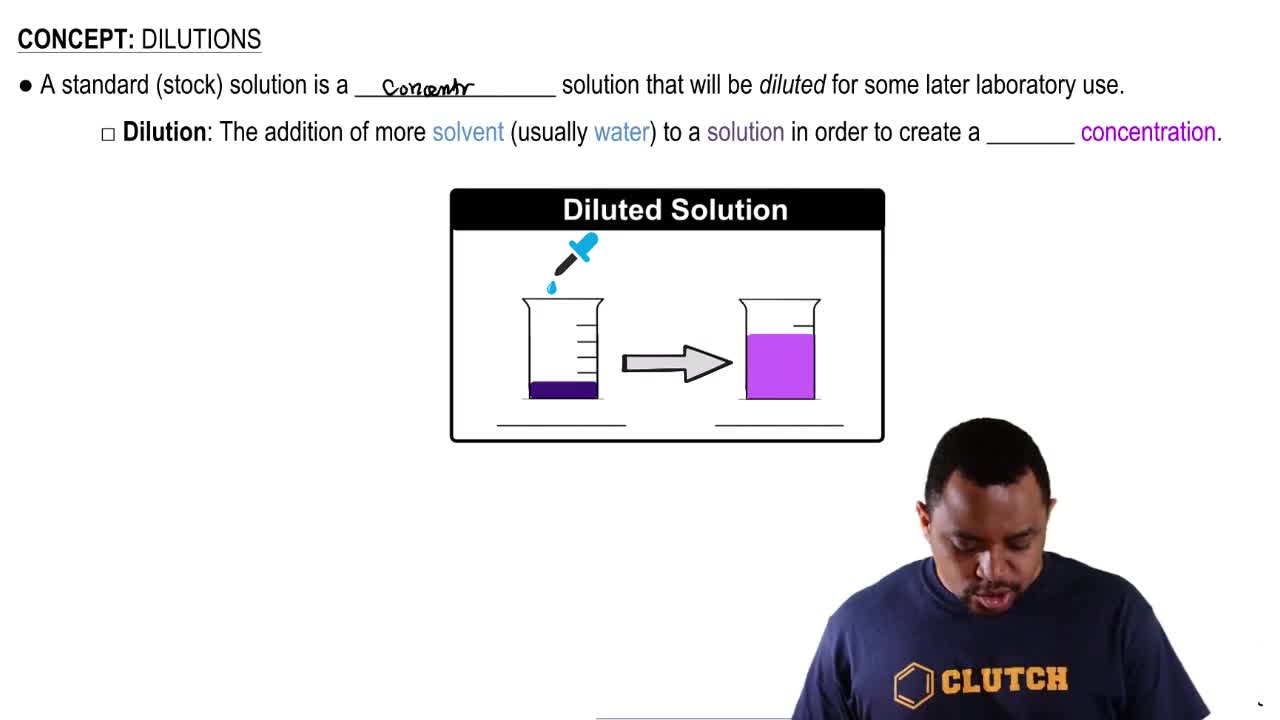
A dilute aqueous solution of boric acid, H3BO3 is often used as an eyewash. How would you prepare 500.0 mL of a 0.50% (m/v) boric acid solution?
What is the mass/volume percent concentration of the following solutions?
a. 0.078 mol KCl in 75 mL of solution
b. 0.044 mol sucrose (C12H22O11) in 380 mL of solution
If you had only 23 g of KOH remaining in a bottle, how many milliliters of 10.0% (m/v) solution could you prepare? How many milliliters of 0.25 M solution?
Nalorphine, a relative of morphine, is used to combat withdrawal symptoms in heroin users. How many milliliters of a 0.40% (m/v) solution of nalorphine must be injected to obtain a dose of 1.5 mg?
Sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) the major component in photographic fixer solution, reacts with silver bromide to dissolve it according to the following reaction:
AgBr(s) + 2 Na2S2O3(aq) → Na3Ag(S2O3)2(aq) + NaBr(aq)
b. How many mL of 0.02 M Na2S2O3 contain this number of moles?
