How many moles of each substance are needed to prepare the following solutions?
a. 50.0 mL of 8.0% (m/v) KCl (MW = 74.55 g/mol)
b. 200.0 mL of 7.5% (m/v) acetic acid (MW = 60.05 g/mol)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

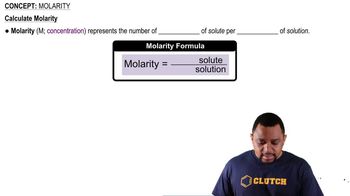
How many moles of each substance are needed to prepare the following solutions?
a. 50.0 mL of 8.0% (m/v) KCl (MW = 74.55 g/mol)
b. 200.0 mL of 7.5% (m/v) acetic acid (MW = 60.05 g/mol)
If you had only 23 g of KOH remaining in a bottle, how many milliliters of 10.0% (m/v) solution could you prepare? How many milliliters of 0.25 M solution?
Nalorphine, a relative of morphine, is used to combat withdrawal symptoms in heroin users. How many milliliters of a 0.40% (m/v) solution of nalorphine must be injected to obtain a dose of 1.5 mg?
An aqueous solution that contains 285 ppm of potassium nitrate (KNO3) is being used to feed plants in a garden. What volume of this solution is needed to prepare 2.0 L of a solution that is 75 ppm in KNO3?
What is the concentration of a NaCl solution, in (m/v)%, prepared by diluting 65 mL of a saturated solution, which has a concentration of 37 (m/v)%, to 480 mL?