Textbook Question
Draw the products you would obtain from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following esters.
b.
708
views

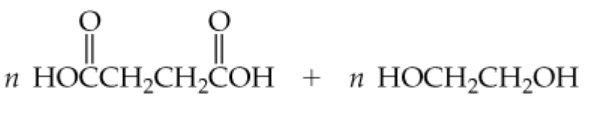
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the products you would obtain from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following esters.
b.
What carboxylic acids and amines result from hydrolysis of the following amides?
a.
What carboxylic acids and amines result from hydrolysis of the following amides?
b. N,N-Dimethyl-p-nitrobenzamide
Write the formula for the phosphate monoester formed from isopropyl alcohol and phosphoric acid.
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
a.
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
b. CH3CH2OPO32-