Cortisol levels rise under stressful conditions. Oxytocin can induce relaxation and romantic feelings. What type of protein are cortisol and oxytocin?

Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a. 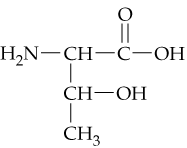
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
α-Amino Acid Structure

Classification of Amino Acids
Role in Protein Synthesis

Consult Table 18.3 and draw alanine. Label the functional groups and give the three-letter abbreviation and the one-letter abbreviation. What group does the side chain fall into?
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
<IMAGE>
Using Table 18.3, name the α-amino acids that (a) contain an aromatic ring, (b) contain sulfur, (c) are alcohols, and (d) have alkyl-group side chains.
Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain and serine is one with a polar side chain. Draw the two amino acids.
a. Why is the side chain for valine nonpolar, whereas the side chain for serine is polar?
Which amino acid is hydrophilic (dissolves in aqueous solutions)? Why?
a. isoleucine
b. phenylalanine
c. aspartic acid
