Consult Table 18.3 and draw alanine. Label the functional groups and give the three-letter abbreviation and the one-letter abbreviation. What group does the side chain fall into?
Ch.18 Amino Acids and Proteins

Chapter 18, Problem 6
Using Table 18.3, name the α-amino acids that (a) contain an aromatic ring, (b) contain sulfur, (c) are alcohols, and (d) have alkyl-group side chains.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. The question asks us to identify α-amino acids based on specific structural features: (a) aromatic rings, (b) sulfur atoms, (c) alcohol groups, and (d) alkyl-group side chains. Refer to Table 18.3 for the list of amino acids and their structures.
Step 2: For part (a), identify amino acids with aromatic rings. Aromatic rings are cyclic structures with alternating double bonds (e.g., benzene). Look for amino acids like phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, which contain aromatic groups in their side chains.
Step 3: For part (b), identify amino acids containing sulfur. Sulfur is present in the side chains of amino acids like cysteine (–SH group) and methionine (–S– group).
Step 4: For part (c), identify amino acids that are alcohols. Alcohol groups are characterized by the –OH functional group. Amino acids like serine and threonine have –OH groups in their side chains.
Step 5: For part (d), identify amino acids with alkyl-group side chains. Alkyl groups are simple hydrocarbon chains or branches. Examples include glycine (H side chain), alanine (–CH₃), valine, leucine, and isoleucine, which all have alkyl groups in their side chains.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Structure
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines its properties. Understanding the structure of amino acids is essential for identifying their classifications based on functional groups.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
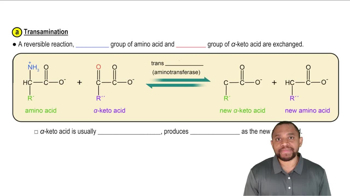
Functional Groups in Amino Acids
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In amino acids, common functional groups include hydroxyl (-OH) for alcohols, thiol (-SH) for sulfur-containing amino acids, and aromatic rings for those with aromatic properties. Recognizing these groups helps in categorizing amino acids based on their side chains.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Concept 2
Classification of Amino Acids
Amino acids can be classified based on the properties of their side chains into categories such as nonpolar, polar, aromatic, and sulfur-containing. This classification is crucial for understanding their roles in protein structure and function. For example, aromatic amino acids like phenylalanine have unique properties due to their ring structure, while sulfur-containing amino acids like cysteine play important roles in protein stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Amino Acid Classifications Example 3
Related Practice
Textbook Question
20
views
Textbook Question
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
<IMAGE>
39
views
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a.
464
views
Textbook Question
Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain and serine is one with a polar side chain. Draw the two amino acids.
a. Why is the side chain for valine nonpolar, whereas the side chain for serine is polar?
888
views
Textbook Question
Which amino acid is hydrophilic (dissolves in aqueous solutions)? Why?
a. isoleucine
b. phenylalanine
c. aspartic acid
807
views
Textbook Question
Is serine chiral? Draw serine and identify the chiral atom. Explain why serine is chiral.
787
views
