Using three-letter abbreviations, show the six tripeptides that contain isoleucine, arginine, and valine.

What atoms are present in a planar unit in a protein chain?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Amino Acids

Peptide Bonds
Planar Structure

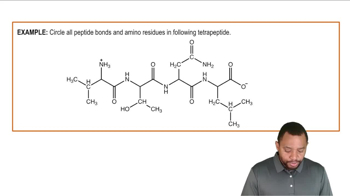
Identify the amino acids in the following dipeptide and tripeptide, and write the abbreviated forms of the peptide names. Copy the dipeptides, draw a box around the peptide bonds, and use an arrow to identify the α-carbon atoms. Draw a circle around the R groups, and indicate if the R groups are neutral, polar, acidic, or basic.
a.
There are eight amino acids in vasopressin. How many peptide bonds are in this small protein?
How many amino acid units do these atoms come from? Why are these units planar?
How many ways can four different amino acids be arranged in a peptide so that each peptide is unique?
Examine the α-helix in Figure 18.1 and determine how many backbone C and N atoms are included in the loop between an amide hydrogen atom and the carbonyl oxygen to which it is hydrogen bonded.
