Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain, and serine is an amino acid with a polar side chain. Draw the two dipeptides that can be formed by these two amino acids. Identify the peptide bond.
Ch.18 Amino Acids and Proteins

Chapter 18, Problem 18a
Identify the amino acids in the following dipeptide and tripeptide, and write the abbreviated forms of the peptide names. Copy the dipeptides, draw a box around the peptide bonds, and use an arrow to identify the α-carbon atoms. Draw a circle around the R groups, and indicate if the R groups are neutral, polar, acidic, or basic.
a. 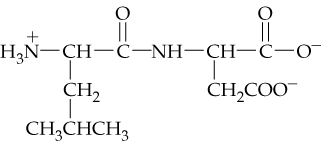
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the structure of peptides. Peptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A dipeptide consists of two amino acids, while a tripeptide consists of three. Each amino acid has an α-carbon, an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a unique R group (side chain).
Step 2: Identify the amino acids in the peptide. Look at the structure provided in the image and locate the repeating units of amino acids. Each amino acid can be identified by its R group, which is unique to each amino acid. Use a reference table of amino acids to match the R groups to their corresponding amino acids.
Step 3: Write the abbreviated form of the peptide name. Use the three-letter or one-letter codes for each amino acid in the sequence. For example, glycine is abbreviated as 'Gly' (three-letter) or 'G' (one-letter). Combine the abbreviations in the order the amino acids appear in the peptide.
Step 4: Highlight the peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next. Draw a box around these bonds in the structure provided. These bonds are typically represented as C(=O)-NH.
Step 5: Identify and classify the R groups. Circle the R groups in the structure and determine their properties. Neutral R groups are nonpolar or uncharged polar, acidic R groups contain a carboxylic acid (-COOH), and basic R groups contain an amino group (-NH2 or similar). Use arrows to point to the α-carbon atoms, which are the central carbons bonded to the amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and R group.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom (α-carbon) bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines its properties. Understanding the structure and classification of amino acids is essential for analyzing peptides.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids together to form peptides and proteins. They are formed through a dehydration synthesis reaction, where the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing a molecule of water. Identifying and illustrating peptide bonds is crucial for understanding the structure of dipeptides and tripeptides.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Peptides Example 1
R Groups and Their Properties
The R group, or side chain, of an amino acid determines its chemical properties and classification as neutral, polar, acidic, or basic. These properties influence the behavior of peptides in biological systems, including their solubility and interactions with other molecules. Analyzing the R groups in the context of the dipeptide and tripeptide is vital for understanding their functional roles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Properties Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
953
views
Textbook Question
Tripeptides are composed of three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Given a set of amino acids, you can make several different tripeptides.
a. Use the three-letter shorthand notations to name all the tripeptides that can be made from serine, tyrosine, and glycine. Each amino acid will be used once in each tripeptide.
558
views
Textbook Question
Using three-letter abbreviations, show the six tripeptides that contain isoleucine, arginine, and valine.
817
views
Textbook Question
There are eight amino acids in vasopressin. How many peptide bonds are in this small protein?
800
views
Textbook Question
What atoms are present in a planar unit in a protein chain?
1580
views
Textbook Question
How many amino acid units do these atoms come from? Why are these units planar?
859
views
