Based on the structure shown for retinol (vitamin A) and the names of the two related forms of vitamin A, retinal and retinoic acid, what do you expect to be the structural differences among these three compounds?
Ch.19 Enzymes and Vitamins

Chapter 19, Problem 25b
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
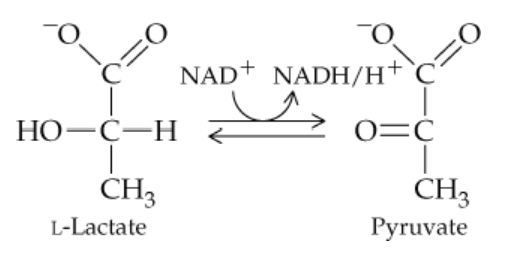
b. Since hydrogens are removed, the enzyme belongs to what subclass of the enzyme class from part (a)?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Recall that enzymes are classified into six major classes based on the type of reaction they catalyze. These classes are oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
Step 2: Understand that the removal of hydrogens from a molecule is typically associated with oxidation reactions. Enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions belong to the oxidoreductase class.
Step 3: Within the oxidoreductase class, there are subclasses based on the specific type of reaction. For example, dehydrogenases are a subclass of oxidoreductases that specifically remove hydrogen atoms from a substrate.
Step 4: Based on the information provided in the problem, identify that the enzyme in question belongs to the dehydrogenase subclass of oxidoreductases, as it is responsible for removing hydrogens.
Step 5: Conclude that the enzyme belongs to the dehydrogenase subclass of the oxidoreductase class, as this aligns with the reaction described in the problem.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enzyme Classification
Enzymes are classified into six main classes based on the type of reaction they catalyze. These classes include oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. Understanding this classification is essential for identifying the specific subclass of an enzyme based on its function in biochemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Six Main Classifications Concept 3
Oxidoreductases
Oxidoreductases are a subclass of enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, where electrons are transferred between molecules. In the context of the question, the removal of hydrogens typically indicates an oxidation process, suggesting that the enzyme in question is likely an oxidoreductase, which plays a crucial role in metabolic pathways.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidoreductases Example 3
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism refers to the step-by-step sequence of events that occur during a chemical reaction, including the formation and breaking of bonds. Understanding the mechanism helps in identifying the role of specific enzymes and the nature of the substrates involved, which is vital for answering questions about enzyme subclasses and their functions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
748
views
Textbook Question
Vitamins are a diverse group of compounds that must be present in the diet. List four functions of vitamins in the body.
652
views
Textbook Question
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
a. The enzyme involved in this reaction belongs to what class of enzymes?
898
views
Textbook Question
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
c. What is the substrate for the reaction as written?
1159
views
Textbook Question
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
d. What is the product for the reaction as written?
1403
views
Textbook Question
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration
1574
views
