Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


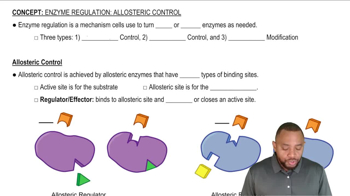
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(b) decreasing the inhibitor concentration at a constant substrate concentration.
Explain how the following mechanisms regulate enzyme activity.
b. Genetic control
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
d. Conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate is inhibited by high levels of ATP. (Hint: ATP is neither a product nor a substrate in this reaction.)
Name the vitamin to which each of these coenzymes is related.
b. Coenzyme A
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
a. Cu2+