Textbook Question
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
a. Buildup of the product of the pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate stops at the first enzyme in the multistep process.
957
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
a. Buildup of the product of the pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate stops at the first enzyme in the multistep process.
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
d. Conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate is inhibited by high levels of ATP. (Hint: ATP is neither a product nor a substrate in this reaction.)
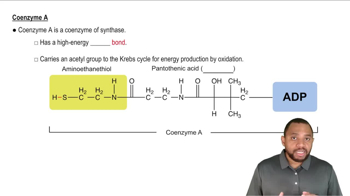
Name the vitamin to which each of these coenzymes is related.
b. Coenzyme A
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
b. Tetrahydrofolate
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
c. NAD+
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
a. Fe2+