Textbook Question
Lactose and maltose are reducing disaccharides, but sucrose is a nonreducing disaccharide. Explain.
944
views

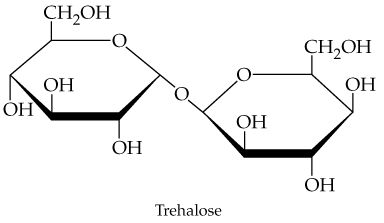
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Lactose and maltose are reducing disaccharides, but sucrose is a nonreducing disaccharide. Explain.
Amylose (a form of starch) and cellulose are both polymers of glucose. What is the main structural difference between them? What roles do these two polymers have in nature?
How are amylose and amylopectin similar to each other, and how are they different from each other?
Are the α and β forms of the disaccharide lactose enantiomers of each other? Why or why not?
D-Fructose can form a six-membered cyclic hemiacetal as well as the more prevalent five-membered cyclic form. Draw the α isomer of D-fructose in the six-membered ring.
Describe the differences between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides.