Textbook Question
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
e. amino acids
590
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
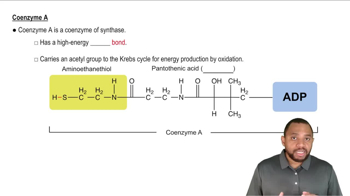
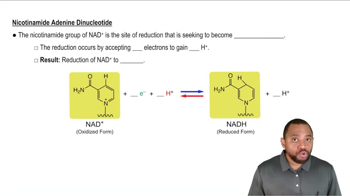
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
e. amino acids
Identify each of the following as a six-carbon or a three-carbon compound and arrange them in the order in which they occur in glycolysis:
a. 3-phosphoglycerate
When is pyruvate converted to lactate in the body?
When pyruvate is used to form acetyl CoA, the product has only two carbon atoms. What happened to the third carbon?
If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?