Back
BackProblem 1
To obtain immediate immunity against tetanus, a patient should receive:
a. An attenuated vaccine of Clostridium tetani
b. A modified live vaccine of C. tetani
c. Tetanus toxoid
d. Immunoglobulin against tetanus toxin (antitoxin)
Problem 2
Which of the following vaccine types is commonly given with an adjuvant?
a. Attenuated vaccine
b. Modified live vaccine
c. Chemically killed vaccine
d. Immunoglobulin
Problem 3
Which of the following viruses was widely used in living vaccines?
a. Coronavirus
b. Poliovirus
c. Influenzavirus
d. Retrovirus
Problem 4
When antigen and antibodies combine, maximal precipitation occurs when:
a. Antigen is in excess
b. Antibody is in excess
c. Antigen and antibody are at equivalent concentrations
d. Antigen is added to the antibody
Problem 5
An anti-antibody is used when:
a. An antigen is not precipitating
b. An antibody is not agglutinating
c. An antibody does not activate complement
d. The antigen is an antibody
Problem 6
The many different proteins in serum can be analyzed by a(n):
a. Anti-antibody test
b. Complement fixation test
c. Precipitation test
d. Immunodiffusion test
Problem 7
A direct fluorescent immunoassay requires which of the following?
a. Heat-inactivated serum
b. Fluorescent serum
c. Immune complexes
d. Antibodies against the antigen
Problem 8
An ELISA uses which of the following reagents?
a. Enzyme-labeled anti-antibody
b. Radioactive anti-antibody
c. Source of complement
d. Enzyme-labeled antigen
Problem 10
Which of the following is a good test to detect rabies virus in the brain of a dog?
a. Agglutination
b. Hemagglutination inhibition
c. Virus neutralization
d. Direct fluorescent antibody
Problem 11
Attenuation is:
a. The process of reducing virulence
b. A necessary step in vaccine manufacture
c. A form of variolation
d. Similar to an adjuvant
Problem 12
An antiserum is:
a. An anti-antibody
b. An inactivated vaccine
c. Formed of monoclonal antibodies
d. The liquid portion of blood used for immunization
Problem 13
Monoclonal antibodies:
a. Are produced by hybridomas
b. Are secreted by clone cells
c. Can be used for passive immunization
d. All of the above
Problem 15
Anti–human antibody antibodies are:
a. Found in immunocompromised individuals
b. Used in direct fluorescent immunoassays
c. Formed by animals reacting to human immunoglobulins
d. An alternative method in ELISA
Problem 1
_______ Passive immunotherapy provides more prolonged immunity than active immunization.
Problem 2
_______ It is standard to attenuate killed virus vaccines.
Problem 3
______ One single serological test is inadequate for an accurate diagnosis of HIV infection.
Problem 4
______ELISA is very easily automated.
Problem 5
______ ELISA has basically replaced immunoblotting.
Problem 1
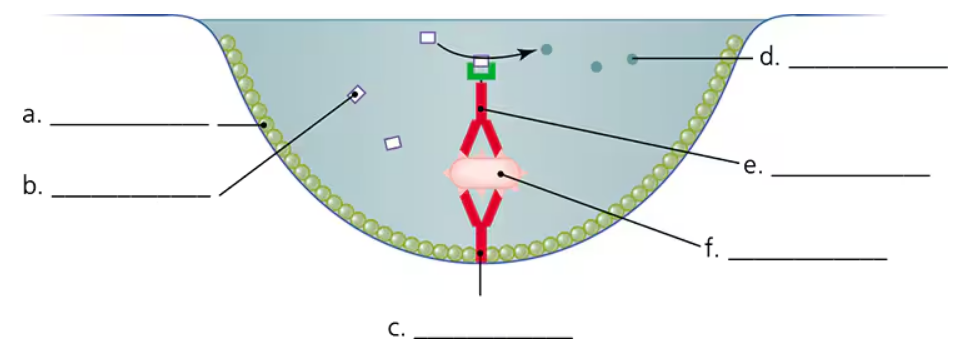
Identify the chemicals represented by this artist’s conception of an antibody sandwich ELISA.
Problem 2
The two columns on the left show negative and positive immunoblot results for a particular pathogen. The numbered columns are blots of samples from 11 patients. Which patients are most likely uninfected?
<IMAGE>
Problem 1
Compare and contrast the Chinese practice of variolation with Jenner’s vaccination procedure.
Problem 2
What are the advantages and disadvantages of attenuated vaccines?
Problem 3
Compare the advantages and disadvantages of passive immunotherapy and active immunization.
Problem 4
How does precipitation differ from agglutination?
Problem 5
Explain how a pregnancy test works at the molecular level.
Problem 6
Compare and contrast herd immunity and contact immunity.
Problem 7
How does nephelometry differ from turbidimetry?